Before I get into the harm that low value pages cause to PageRank; what do I actually mean? Low value pages are defined by Google as redundant, possibly copied, shallow in value, or irrelevant to the search term. It is an issue that affects a lot of retailers and is something that needs to be addressed in order to improve a website ranking. The most common examples of this we see on retail sites are:
- Linking to 1 and 2 star rating pages
- One product facets
- Facets with zero search volume and no statistical significance
- Pick up in store / Click and Collect filters (very common nowadays)
- Price filtered pages
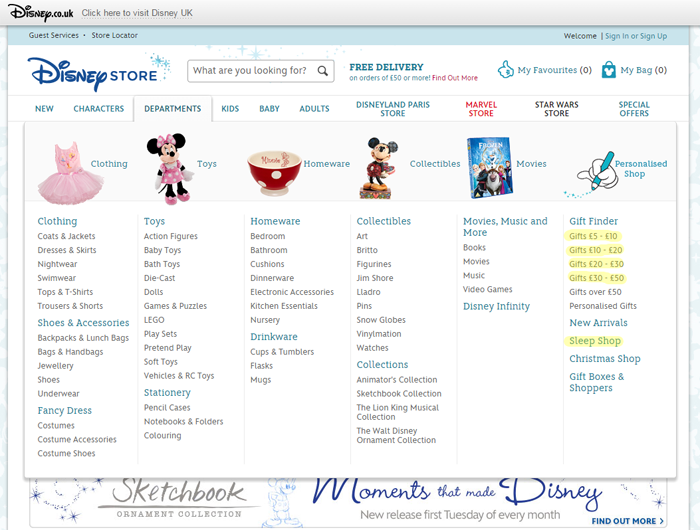
Disney Store is a prime example where there are a number links to low value pages in the MegaNav, with very little or no search volume, that have been indexed by Google.
These low value pages soak up PageRank and link equity from within a website, leaving less equity to be shared across the high value pages. This is done through MegaNavs, as in this example, and faceted navigation. Faceted navigation is a great tool for user experience (UX), but left to its own devices, multiplies the number of pages on your website exponentially and begins to undermine your SEO by leaking out vital page rank away from pages that need it.
One retailer we recently analysed has 4,000 products, but all the linking to facets and redundant pages meant that search engines crawled and indexed over 1 million pages. This forces crawlers to burn up their bandwidth and miss the high value pages actually being searched for.
For example if we take a look at a Toys page, we want the Toys page to link to our Frozen Toys page, our Soft Toys page, and to our Baby Toys. The problem arises when the Toys page also links to the one-star customer rated Toys page, the toys between £20-£30, and the Pick-up in Store page, which is not what your customer is searching for.
However, because our Toys page is linking them to multiple low value pages, the link equity is being bled down away from the pages that we do actually want to rank. Unfortunately, that’s just how most sites are organised, and as a result, the high value pages actually rank more poorly. This is happening in every single category and sub-category right across the site, meaning every page is ranking poorer for its keywords then it otherwise would have had the link equity not been shared so indiscriminately.
To preserve your link equity you first have to identify the low values pages across your website and apply targeted redirects and canonical tags in order to help search engines identify where they don’t need to go. As a result, with less junk to crawl through, your site and all its valuable pages can now be crawled more comprehensively. This means low value pages are saved from crawlers’ routines, each page’s link equity can be distributed to the pages that users are searching, which then improves the search experience and drives more traffic, and most importantly, revenue to your business.